Pleiotropy
from Greek πλείων pleion,
'more'
and τρόπος tropos,
'way'
Today’s post introduces a new term –
SGLT2.
Depending how old you are, you will be
aware of the term BFF – Best Friend Forever.
These days you can have several BFFs, not just one.
Pleiotropy (play-o-tropy) is a rather
nice sounding word that was brought into use in science and medicine by a
German geneticist Ludwig Plate in 1910. Pleiotropic effects of a drug are any beneficial
secondary effects.
Statins are the classic example. They
were developed to lower cholesterol, but many of the positive effects
experienced by users have nothing to do with cholesterol, they lower
inflammation (and more besides). It is now thought that inflammation in your arteries triggers a protective layer of cholesterol to be deposited. As the decades pass, this protective layer grows and ends up causing all kinds of problems.
When you repurpose an old drug for a
new use, you are taking advantage of its pleiotropic effects. For readers of this blog pleiotropy is a
friend, and quite possibly a BFF.
SGLT2
Today we look at repurposing a class
of drugs that lowers blood sugar for those with type 2 diabetes to treat a wide
range of brain disorders.
We also look at a cheap pain killer
that can be used to disrupt an inflammatory pathway key to most brain disorders
and even some cancers.
Our reader Eszter did recently highlight a very well written paper
about the potential to repurpose SGLT2 inhibitors to treat autism.
Eszter knows a lot about neurology, I should point out.
Eszter
has previously commented on the interesting overlap between drugs that provide
a benefit in Alzheimer’s and those that benefit some autism. She will likely find the link at the very end of this post of interest.
Repurposing SGLT2 Inhibitors for Neurological
Disorders: A Focus on the Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a
neurodevelopmental disorder with a substantially increasing incidence rate. It
is characterized by repetitive behavior, learning difficulties, deficits in
social communication, and interactions. Numerous medications, dietary
supplements, and behavioral treatments have been recommended for the management
of this condition, however, there is no cure yet. Recent studies have examined
the therapeutic potential of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2)
inhibitors in neurodevelopmental diseases, based on their proved
anti-inflammatory effects, such as downregulating the expression of several
proteins, including the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), interleukin-6
(IL-6), C-reactive protein (CRP), nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), tumor necrosis
factor alpha (TNF-α), and the monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP-1).
Furthermore, numerous previous studies revealed the potential of the SGLT2
inhibitors to provide antioxidant effects, due to their ability to reduce the
generation of free radicals and upregulating the antioxidant systems, such as
glutathione (GSH) and superoxide dismutase (SOD), while crossing the blood
brain barrier (BBB). These
properties have led to significant improvements in the neurologic outcomes of
multiple experimental disease models, including cerebral oxidative stress in
diabetes mellitus and ischemic stroke, Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's
disease (PD), and epilepsy. Such diseases have mutual biomarkers with
ASD, which potentially could be a link to fill the gap of the literature
studying the potential of repurposing the SGLT2 inhibitors' use in ameliorating
the symptoms of ASD. This review will look at the impact of the SGLT2
inhibitors on neurodevelopmental disorders on the various models, including
humans, rats, and mice, with a focus on the SGLT2 inhibitor canagliflozin.
Furthermore, this review will discuss how SGLT2 inhibitors regulate the ASD
biomarkers, based on the clinical evidence supporting their functions as
antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents capable of crossing the blood-brain
barrier (BBB).
Recently I was asked by one researcher
reader where is the evidence to support my suggestion that Ponstan (Mefenamic
Acid) can enhance cognition. I was not
sure that I would find evidence that relates to actual humans, but I did. This
took me back to the time this blog looked into the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Just like the new generation of type 2
diabetes drugs have pleiotropic effects on the brain, so do Fenamate class
NSAIDs, specifically Ponstan.
There are four SGLT2 inhibitors approved to treat type 2 diabetes
·
Invokana
(canagliflozin)
·
Farxiga
(dapagliflozin)
·
Jardiance
(empagliflozin)
·
Steglatro
(ertugliflozin)
To be effective inside the brain such
a drug would need to be small and lipid (fat soluble) enough to get across the
blood brain barrier.
If the idea of a diabetes drug helping
brain disorders sounds strange, consider what we have already come across in
previous posts in this blog.
Other Type 2
drugs with pleiotropic effects
Metformin
Metformin was discovered exactly 100
years ago, in 1922. It is not a new drug
and it is the world’s most common therapy for type 2 diabetes.
It has been suggested metformin can
delay the onset of aging and also the onset and development of Alzheimer’s.
The use
of metformin has repeatedly associated with the decreased risk of the
occurrence of various types of cancers, especially of the pancreas and colon
and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Metformin
has been shown to raise IQ in children with Fragile-X syndrome by about 10%.
Some
people with autism do take metformin, in others it provides no benefit.
Glitazones
Glitazones
are a class of anti-diabetic drug that started to get popular from the year
2000. They work by stimulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
gamma (PPAR-γ) receptor. They will activate PGC-1 alpha, which we know is the key
regulator of mitochondrial
biogenesis. For some strange reason, glitazone drugs are not used to treat
mitochondrial disease.
Glitazones
have broad anti-inflammatory pleiotropic effects.
Pioglitazone
has been researched in autism and I have used it for several years as a spring
and summertime add-on therapy in Monty’s PolyPill.
Back to Eszter’s
paper
I highlight some of the tables, which
do summarize the beneficial effects.
Inflammatory signals promote inflammation by
activating the microglia and astrocytes within the brain in ASD. SGLT2
inhibitors influence on the inflammation and neuroinflammation, SGLT2 inhibitors decrease the
inflammatory factors levels, such as the M1 macrophages, STAT1 inflammatory
transcription factor, cytokine interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor
(TNF-α), and vascular cell adhesion protein (VCAM) in neurodevelopmental
diseases
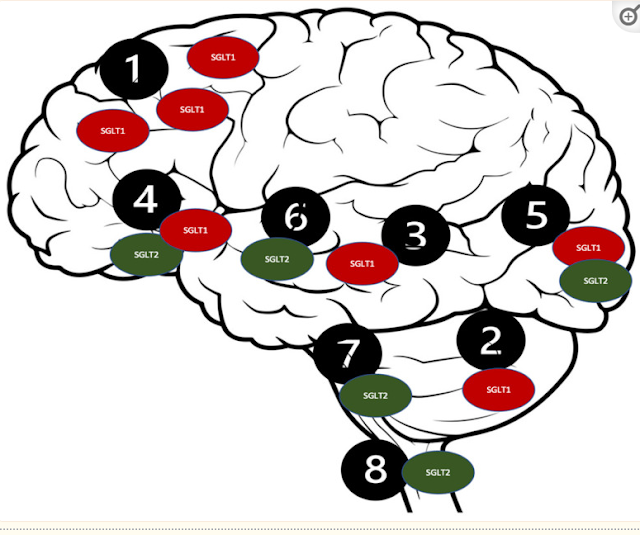
Distribution of the SGLT receptors in the
CNS. 1. Brain cortex (pyramidal cells); 2. Purkinje neurons; 3. Hippocampus; 4.
Hypothalamus; 5. Micro vessels; 6. Amygdala cells; 7. Periaqueductal gray; 8.
Dorsomedial medulla.
Such a
distribution of the SGLT2 receptors [114] could
potentially be responsible for their intriguing neuroprotective qualities,
which could be beneficial in several neurological disorders, including ASD [99]. The SGLT2
inhibitors’ proposed mechanisms are presented in Figure
3. The
antioxidant effect of the SGLT2 inhibitors can be attributed to their
stimulatory action on the nuclear factor erythroid 2 (Nrf2)- related factor 2
pathway [115]. This
displays the antioxidant activity because of their genetic expression of the
antioxidant proteins, including glutathione-s-transferase (GST), SOD, and NADPH
quinone dehydrogenase-1 to protect against cellular apoptosis [116]. The
anti-inflammatory characteristics of the SGLT2 inhibitors could be accredited
to the downregulation of NF-KB, which decreases IL-1β and the TNF-α expression
[117].
Empagliflozin has the highest selectivity for the SGLT2 receptors (2500-fold)
when compared to dapagliflozin which has (1200-fold) selectivity, and
canagliflozin (250-fold) [118,119]. Therefore, in the context of the
neuroprotective effects associated with the SGLT1 and SGLT2 receptors’
inhibition, canagliflozin was hypothetically preferred over other SGLT2
inhibitors, due to its dual SGLT1/SGLT2 inhibition capability [120].
SGLT2 inhibitors have the potential to
improve ASD patients’ behavioral and brain disruptions by increasing the
cerebral brain derived neurotrophic factor and reducing the cerebral oxidative
stress, including elevated the GSH and catalase activity, reduced MDA, amyloid
β levels, plaque density, and acetylcholinesterase
ASD
remains a global health dilemma, as it is a chronic condition, and is
incurable, leading to a reduced quality of life. It is crucial to find the
mutual molecular mechanisms of ASD and redefine the indications for the
well-studied medication with numerous pleiotropic effects to find a solution.
This review has disclosed the impact of the SGLT2 inhibitors in neurological
diseases, which could relate to ASD as it shares multiple pathways and mutual
biomarkers. SGLT2 inhibitors display several neuroprotective properties,
highlighting their therapeutic potential for ASD patients, as these agents have
the capability to inhibit the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, reduce the elevated
levels of the oxidative stress in the brain, and restore the anabolism and
catabolism balance. Moreover, clinical intervention studies are vital to
determine whether the displayed methods are useful as the SGLT2 inhibitors have
never been tested on ASD directly. Currently, our research team is conducting a
preclinical experiment to assess the effects of canagliflozin on the
VPA-induced ASD in Wistar rats.
Back to the NLRP3
Inflammasome
Ponstan (Mefenamic acid) is one of the
few available drugs that is known to be a potent inhibitor of an inflammatory
pathway called the NLRP3 inflammasome. It
is mainly present macrophages, a type of white blood cell in the immune system. The role of macrophages includes gobbling up
pathogens.
In the brain the microglia
are the resident macrophages. The
microglia have multiple functions in the brain and we know that in autism they
can be stuck in an overactivated state and then do not fulfil their other functions.
In many diseases activation of the NLRP3
inflammasome in local macrophages occurs.
Inhibiting this process can disrupt the disease process.
My guess is that this is the mechanism
by which Ponstan is improving cognition in some of the people with autism who
are taking it.
In the paper below we see that people
taking Ponstan to treat their prostate cancer (PCa) experience an improvement
in their cognition.
Inflammation
is an essential component of prostate cancer (PCa), and mefenamic acid has been
reported to decrease its biochemical progression. The current standard therapy for PCa is
androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), which has side effects such as cognitive
dysfunction, risk of Alzheimer’s disease, and dementia. Published results of in
vitro tests and animal models studies have shown that mefenamic acid could be
used as a neuroprotector. Objective: Examine the therapeutic potential of mefenamic acid in cognitive
impairment used in a controlled clinical trial. Clinical trial phase II
was conducted on patients undergoing ADT for PCa. Two groups of 14 patients
were included. One was treated with a placebo, while the other received
mefenamic acid 500 mg PO every 12hrs for six months. The outcome was evaluated
through the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score at six months. At the
beginning of the study, both groups had similar MMSE scores (mefenamic acid vs.
placebo: 26.0±2.5 vs. 27.0±2.6, P=0.282). The mefenamic acid group improved its
MMSE score after six months compared with the placebo group (27.7±1.8 vs.
25.5±4.2, P=0.037). Treatment
with mefenamic acid significantly increases the probability of maintained or
raised cognitive function compared to placebo (92% vs. 42.9%, RR=2.2,
95% CI: 1.16-4.03, NNT=2.0, 95% CI: 1.26-4.81, P=0.014). Furthermore, 42.9% of
the placebo group patients had relevant cognitive decline (a 2-point decrease
in the MMSE score), while in patients treated with mefenamic acid, cognitive
impairment was not present. This
study is the first conducted on humans that suggests that mefenamic acid
protects against cognitive decline.
In the AEA mouse model of MS (multiple
sclerosis) we see the role again of NLRP3 on cognition.
Some studies have indicated that NLRP3 inflammasome activation is
involved in mediating synaptic dysfunction, cognitive impairment, and
microglial dysfunction in AD models, and that the inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome
attenuates spatial memory impairment and enhances Aβ clearance in AD
model. However, there is no research on NLRP3 inflammasome in MS-related
cognitive deficits. In our study, we found that microglia and NLRP3 inflammasome were activated in the
hippocampus of EAE mice, while pretreatment with MCC950 inhibited the
activation of microglia and NLRP3 inflammasome
Again, we see a benefit from
inhibiting NLRP3 in Alzheimer’s.
Aberrant activation of the Nod-like receptor
family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome plays an essential role
in multiple diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and psoriasis. We
report a novel small-molecule inhibitor, NLRP3-inhibitory compound 7 (NIC7),
and its derivative, which inhibit NLRP3-mediated activation of caspase 1 along
with the secretion of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-18, and lactate dehydrogenase. We
examined the therapeutic potential of NIC7 in a disease model of AD by
analyzing its effect on cognitive impairment as well as the expression of
dopamine receptors and neuronal markers. NIC7 significantly reversed the
associated disease symptoms in the mice model. On the other hand, NIC7 did not
reverse the disease symptoms in the imiquimod (IMQ)-induced disease model of
psoriasis. This indicates that IMQ-based psoriasis is independent of NLRP3.
Overall, NIC7 and its derivative have therapeutic prospects to treat AD or
NLRP3-mediated diseases.
What about sepsis (blood poisoning)?
The
pathophysiology of sepsis may involve the activation of the NOD-type receptor
containing the pyrin-3 domain (NLPR-3), mitochondrial and oxidative damages. One of the
primary essential oxidation products is 8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG), and its
accumulation in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) induces cell dysfunction and death,
leading to the hypothesis that mtDNA integrity is crucial for maintaining neuronal
function during sepsis. In sepsis, the modulation of NLRP-3 activation is
critical, and mefenamic
acid (MFA) is a potent drug that can reduce inflammasome activity, attenuating
the acute cerebral inflammatory process. Thus, this study aimed to evaluate
the administration of MFA and its implications for the reduction of
inflammatory parameters and mitochondrial damage in animals submitted to
polymicrobial sepsis. To test our hypothesis, adult male Wistar rats were
submitted to the cecal ligation and perforation (CLP) model for sepsis
induction and after receiving an injection of MFA (doses of 10, 30, and
50 mg/kg) or sterile saline (1 mL/kg). At 24 h after sepsis
induction, the frontal cortex and hippocampus were dissected to analyze the
levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-18; oxidative damage (thiobarbituric acid
reactive substances (TBARS), carbonyl, and DCF-DA (oxidative parameters);
protein expression (mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM), NLRP-3,
8-oxoG; Bax, Bcl-2 and (ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 (IBA-1));
and the activity of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes. It was observed
that the septic group in both structures studied showed an increase in
proinflammatory cytokines mediated by increased activity in NLRP-3, with more significant
oxidative damage and higher production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by
mitochondria. Damage to mtDNA it was also observed with an increase in 8-oxoG
levels and lower levels of TFAM and NGF-1. In addition, this group had an
increase in pro-apoptotic proteins and IBA-1 positive cells. However, MFA at
doses of 30 and 50 mg/kg decreased inflammasome activity, reduced levels
of cytokines and oxidative damage, increased bioenergetic efficacy and reduced
production of ROS and 8-oxoG, and increased levels of TFAM, NGF-1, Bcl-2,
reducing microglial activation. As a result, it is suggested that MFA oinduces protection in the central
nervous system early after the onset of sepsis.
Conclusion
One reader of this blog attributes her
son’s autism to his sepsis (blood poisoning) at birth. It is pretty clear from
one of today’s papers that perhaps babies with sepsis should be treated with
Ponstan (Mefenamic acid) to prevent damage to their brain. I was recently contacted by another parent where sepsis occurred at birth.
I think the researchers make a strong
case that the pleiotropic effects of SGLT2 inhibitors that benefit Alzheimer’s,
Parkinson’s and ALS very likely will also be beneficial in some autism. They plan to test canagliflozin on rats with
valproic acid-induced autism.
I have to say to Eszter that I
actually think inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome might be the Neurologist’s
best friend forever (BFF), perhaps even better than an SGLT2 inhibitor.
What is for sure is that both (SGLTi
and NLRP3i) should be subject of clinical trials in autism. I suggest going
straight humans rather than rats.
I have had positive feedback so far on
my suggestion that low dose (250 mg) Ponstan/Mefenamic acid could be an
effective long term autism therapy. We
do have to mention that Knut Wittkowski has patented its use in autism; he
proposed it as a preventive measure in 2-3 year olds to redirect severe
non-verbal autism towards Asperger’s. I selected it to treat extreme sound
sensitivity, but later witnessed its pleiotropic effects.
If anyone has experience on the use of
an SGLT2 inhibitor in autism, I would be very interested to read about it.
We should add Ponstan to the long list
of drugs in this autism blog that may be beneficial in MS (Multiple sclerosis).
(ALA, Clemastine, NAG, Ibudilast, DMF, Ponstan etc).
P.S.
A last word from
Google
Having noted my recent googling
activity, I was today sent the following news item by Google.
Harnessing the
Brain’s Immune Cells to Stave off Alzheimer’s and Other Neurodegenerative
Diseases
Researchers have identified a protein that
could be leveraged to help microglia in the brain stave off Alzheimer’s and
other neurodegenerative diseases
But how does SYK protect the nervous system
against damage and degeneration? We found that microglia use SYK to migrate
toward debris in the brain. It also helps microglia remove and destroy this
debris by stimulating other proteins involved in cleanup processes. These jobs
support the idea that SYK helps microglia protect the brain by charging them to
remove toxic materials.